Rozpowszechnienie SSc‑ILD
Śródmiąższowa choroba płuc (ILD) jest wczesną i częstą manifestacją twardziny układowej (SSc)1,2



ILD CZĘSTO ROZWIJA SIĘ NA WCZESNYM ETAPIE PRZEBIEGU SSc1,5–7
Ryzyko rozwoju ILD jest największe we wczesnym okresie przebiegu SSc.6 U niektórych pacjentów pierwszy objaw kliniczny SSc jest bezpośrednio związany z ILD.7,8 ILD może rozwinąć się w ciągu roku od wystąpienia objawu Raynauda.1
ILD często rozwija się na wczesnym etapie przebiegu SSc1
Wśród 695 pacjentów z SSc, u których wizyta wyjściowa odbyła się w ciągu 1 roku od wystąpienia zjawiska Raynauda, u 31% pacjentów FVC wynosiła <80% wartości należnej, a u 65% DLCO wynosiła <80% wartości należnej.1
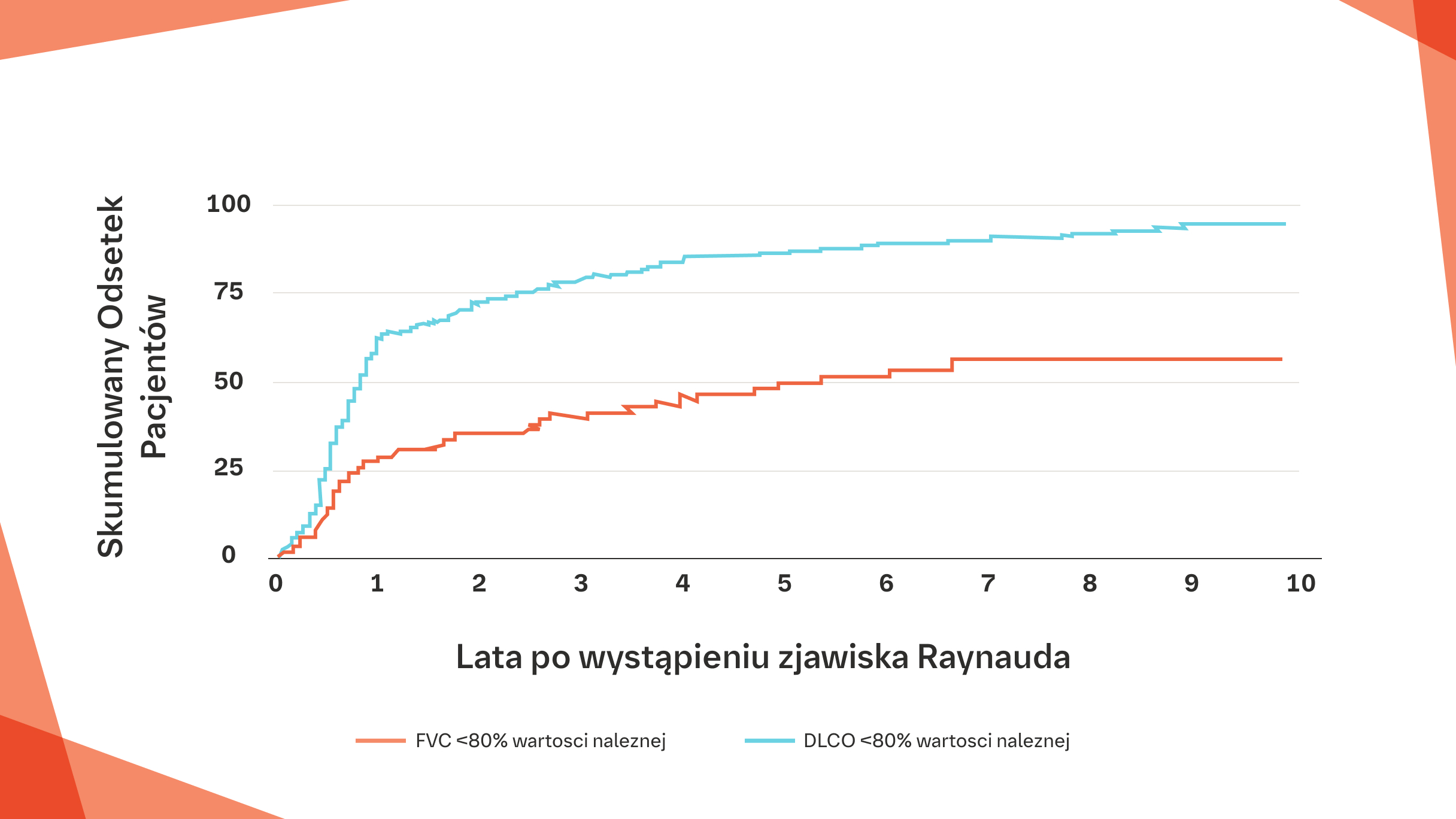
Na podstawie: Jaeger VK i wsp. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e01638.
STARSZY WIEK, PŁEĆ MĘSKA I POCHODZENIE AFRYKAŃSKIE – TO NIEKTÓRE Z KLUCZOWYCH CZYNNIKÓW, KTÓRE ZWIĘKSZAJĄ PRAWDOPODOBIEŃSTWO ROZWOJU ILD U PACJENTÓW Z SSc5,8
Średni wiek w chwili rozpoznania SSc-ILD wynosi 54,5 roku.9 Pomimo znacznej przewagi kobiet w SSc (stosunek kobiet do mężczyzn równy 4,7:1), ILD częściej rozwija się u mężczyzn z SSc.7 Obecność dcSSc jest również czynnikiem ryzyka rozwoju ILD.8
Cechy typowego pacjenta związane z rozwojem ILD w przebiegu SSc5,8



Jaki wpływ może mieć ILD na pacjentów z SSc i jak można zidentyfikować to zagrożenie?
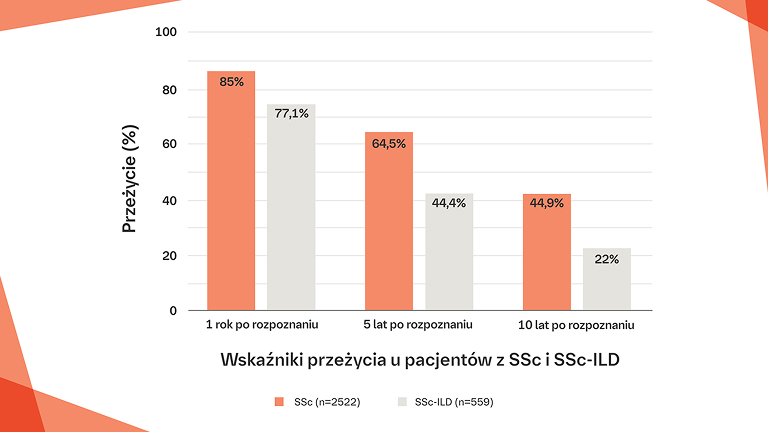
Skutki SSc‑ILD
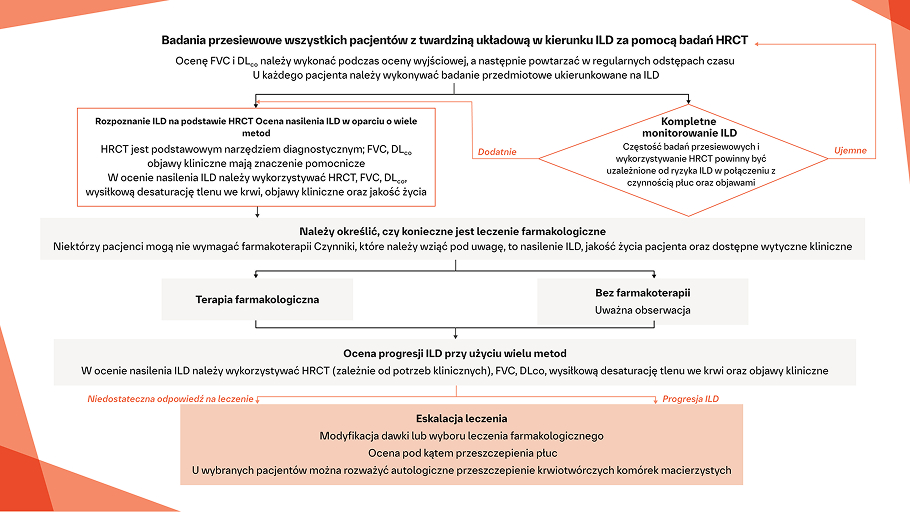
Badania przesiewowe w kierunku ILD w przebiegu CTD
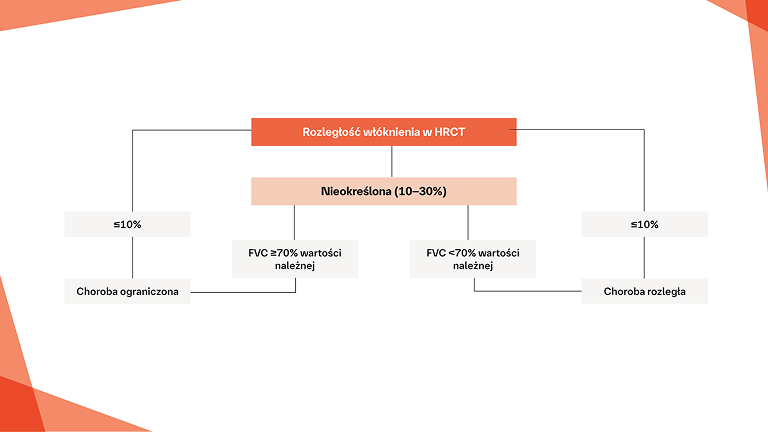
Rozpoznanie CTD‑ILD
Przypisy
-
CTD: choroba tkanki łącznej; CTD-ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc związana z chorobą tkanki łącznej; HRCT: tomografia komputerowa wysokiej rozdzielczości; ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc.
-
Jaeger VK, Wirz EG, Allanore Y, et al. Incidences and risk factors of organ manifestations in the early course of systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal EUSTAR study. PLoS ONE. 2016;11;e0163894.
-
Lescoat A, Huscher D, Hachulla E, et al. Prevalence and clinical presentation of SSc-associated ILD according to worldwide spatial repartition in the EUSTAR database. Poster presented at the 6th Systemic Sclerosis World E-Congress 2020.
-
Walker UA, Tyndall A, Czirjak L, et al. Clinical risk assessment of organ manifestations in systemic sclerosis: a report from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials And Research group database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66(6):754–63.
-
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Fretheim H, Halse AK, et al. Tracking impact of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis in a complete nationwide cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200;1258–1266.
-
Cottin V, Brown KK. Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc-ILD). Respir Res. 2019;20;13.
-
Denton CP, Khanna D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet. 2017;390;1685–1699.
-
Distler O, Assassi S, Cottin V, et al. Predictors of progression in systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J. 2020;55;1902026.
-
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Allanore Y, Alves M, et al. Progressive interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis- associated interstitial lung disease in the EUSTAR database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. Epub ahead of print: doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217455.
-
Ryerson CJ, O’Connor D, Dunne JV, et al. Predicting mortality in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease using risk prediction models derived from idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 2015;148;1268–1275.
-
Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69;1809–1815.
-
Asano Y, Jinnin M, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Diagnostic criteria, severity classification and guidelines of systemic sclerosis: Guideline of SSc. J Dermatol. 2018;45;633–691.
-
Denton C, Hughes M, Gak N et al. BSR and BHPR guideline for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology. 2016;55;1906–1910.
-
Roofeh D, Jaafar S, Vummidi D, et al. Management of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31;241–249.
-
Fischer A, Patel NM, Volkmann ER. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: focus on early detection and intervention. OARRR. 2019;11;283–307.
Materiały dla pacjentów po angielsku




