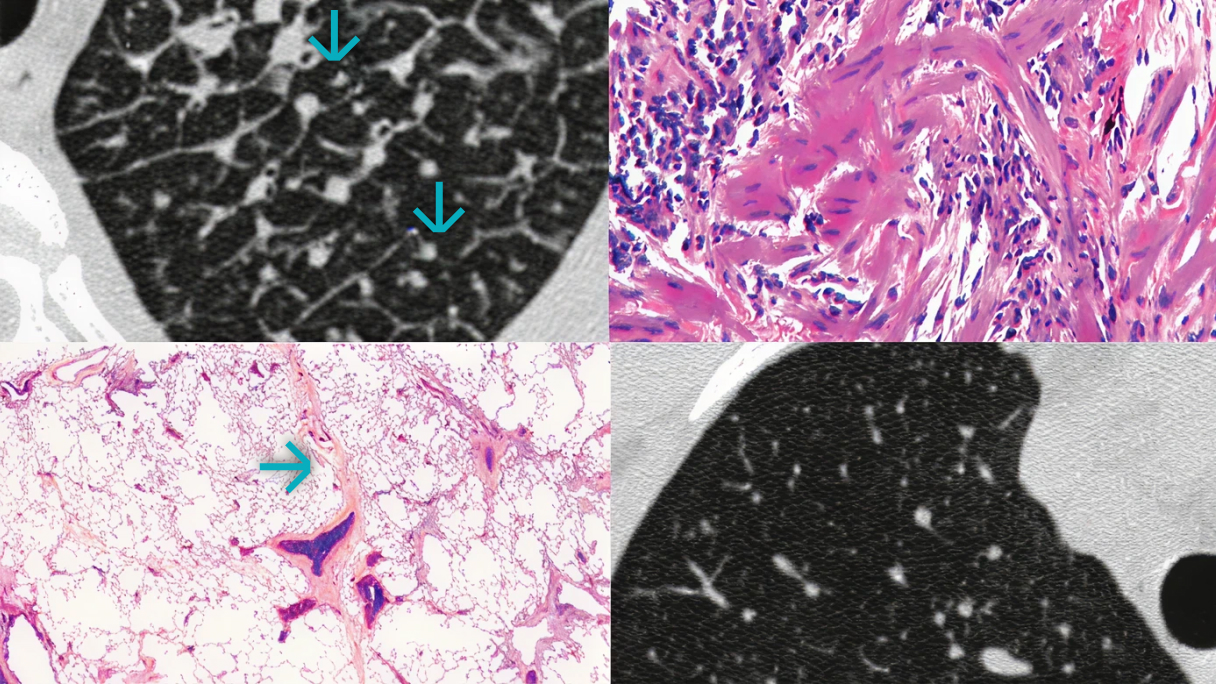
ROZWAŻ ROZPOZNANIE WŁÓKNIENIA PŁUC
Śródmiąższowa choroba płuc (ILD) często bywa wczesną manifestacją CTD, która ma wspólne ścieżki patogenetyczne z włóknieniem.1-7 Możesz spotkać pacjentów z chorobami tkanki łącznej (CTD), u których rozwija się ILD, w tym włóknienie płuc.

DOWIEDZ SIĘ, DLACZEGO I W JAKI SPOSÓB IDENTYFIKACJA WŁÓKNIEJĄCEJ CTD‑ILD MA ZNACZENIE

Badania przesiewowe w kierunku ILD w przebiegu CTD
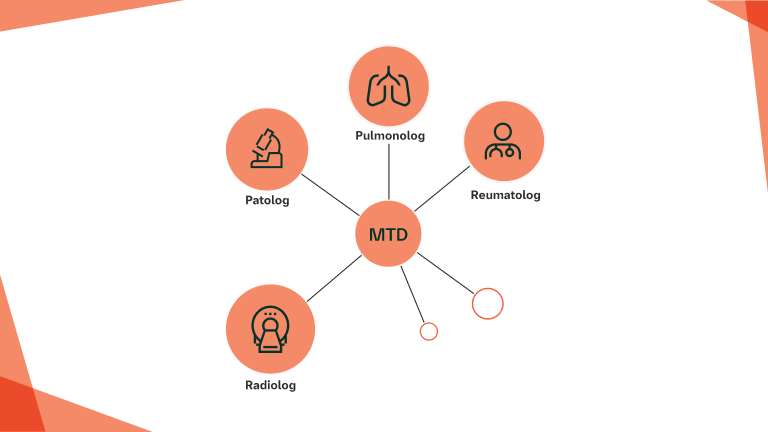
Rozpoznanie CTD‑ILD
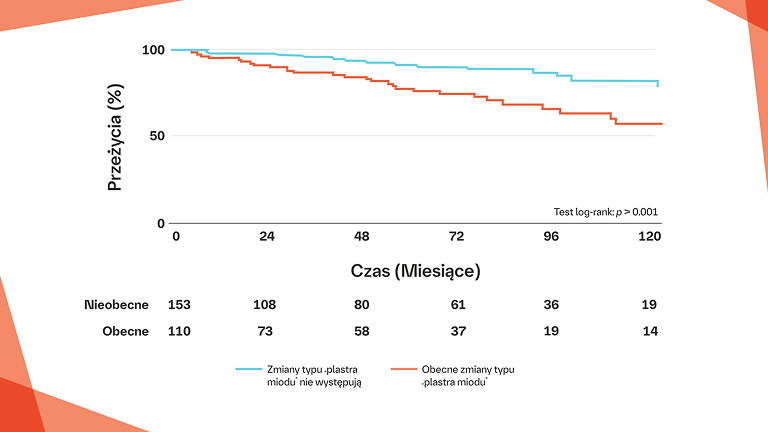
Zwiększone wskaźnikiśmiertelności
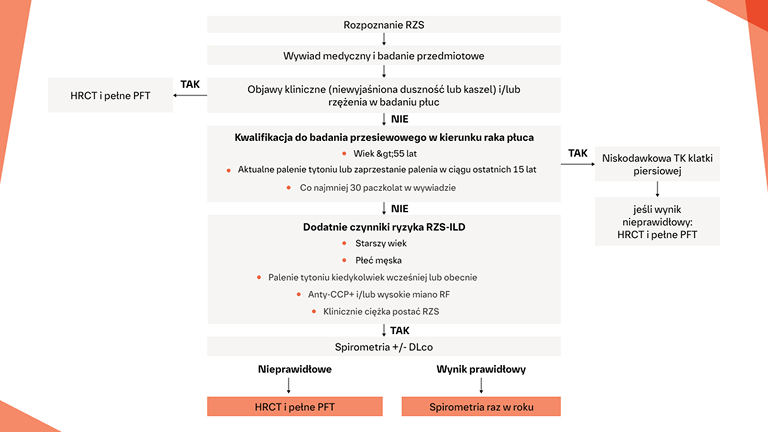
Badania przesiewowe w kierunku ILD w RZS
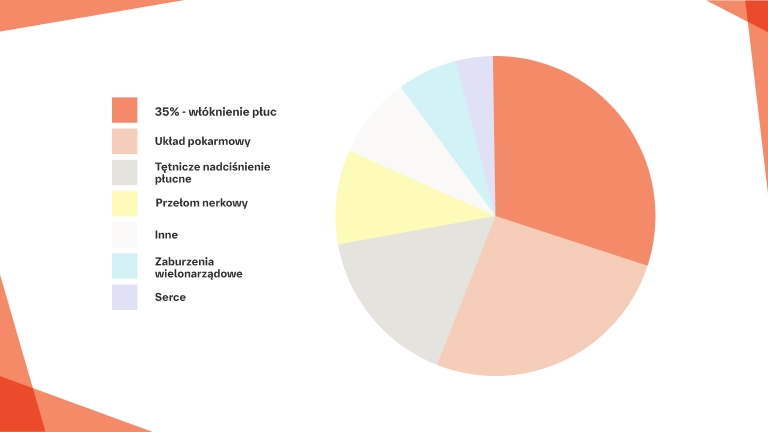
Leczenie SSc‑ILD

Model SPIKES: przekazywanie pacjentom niepomyślnych wiadomości
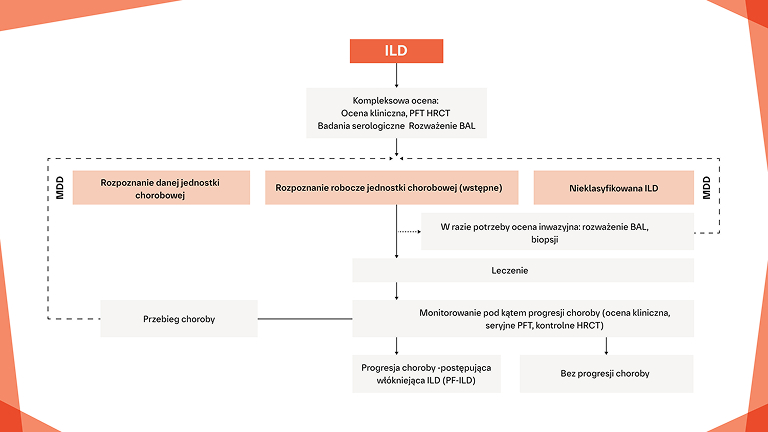
Wczesne i regularne monitorowanie pod kątem progresji ILD w CTD‑ILD

Opisy przypadków pacjentów z CTD‑ILD do oceny przesiewowej i diagnostyki
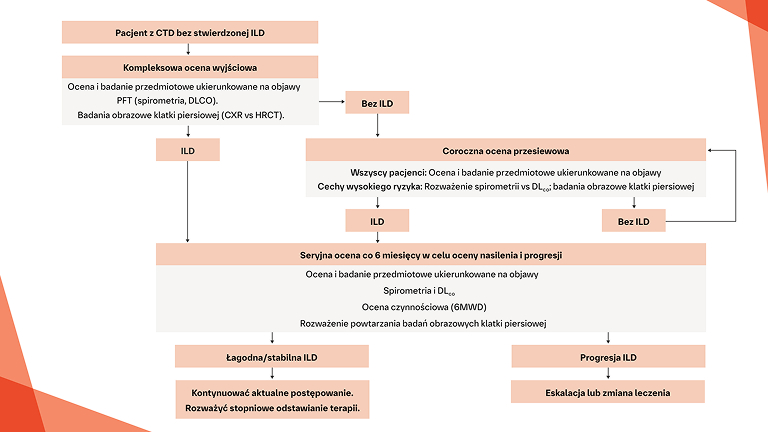
Postępowanie w postępującej włókniejącej CTD‑ILD
Przypisy
-
CTD: choroba tkanki łącznej; CTD-ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc związana z chorobą tkanki łącznej; HRCT: tomografia komputerowa wysokiej rozdzielczości; ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc; RZS-ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc związana z reumatoidalnym zapaleniem stawów; RZS: reumatoidalne zapalenie stawów; SSc: twardzina układowa; SSc-ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc związana z twardziną układową.
-
Fischer A and Distler J. Progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease associated with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(10):2673–2681.
-
Mathai SC and Danoff SK. Management of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. BMJ. 2016;352:h6819.
-
Wallace B, Vummidi D, Khanna D. Management of connective tissue diseases associated interstitial lung disease: a review of the published literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(3):236–245.
-
Spagnolo P, Cordier JF, Cottin V. Connective tissue diseases, multimorbidity and the ageing lung. Eur Respir J. 2016;47(5):1535–1558.
-
Vacchi C, Sebastiani M, Cassone G, et al. Therapeutic options for the treatment of interstitial lung disease related to connective tissue diseases. A narrative review. J Clin Med. 2020;9(2):407. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020407.
-
Koo SM, Kim SY, Choi SM, et al. Korean guidelines for diagnosis and management of interstitial lung diseases: part 5. Connective tissue disease associated interstitial lung disease. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2019;82(4):285–297.
-
Doyle TJ, Hunninghake GM, Rosas IO. Subclinical Interstitial Lung Disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;185:1147–1153.
-
Maher TM, Wuyts W. Management of fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Adv Ther. 2019;36(7):1518–1531.
-
Esposito AJ, Chu SG, Madan R, et al. Thoracic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chest Med. 2019;40(3):545–560.
-
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Allanore Y, Alves M, et al. Progressive interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis- associated interstitial lung disease in the EUSTAR database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020. Epub ahead of print: doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217455.
-
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Maher TM, Philpot EE, et al. The identification and management of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: evidence-based European consensus statements. Lancet Rheum. 2020;2 e71–e83.
-
Distler O, Volkmann ER, Hoffmann-Vold AM, et al. Current and future perspectives on management of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2019;15:1009–1017.
-
Chowaniec M, Skoczyńska M, Sokolik R, Wiland P. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: challenges in early diagnosis and management. Reumatologia. 2018;56(4):249–254.
-
Cottin V, Brown KK. Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc–ILD). Respir Res. 2019a;20(1):13.
-
Geerts S, Wuyts W, de Langhe E, et al. Connective tissue disease associated interstital pneumonia: a challenge for both rheumatologists and pulmonologists. Sarcoidosis Vasc Dif. 2017;34:326–335.
-
Wells AU, Denton CP. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disease—mechanisms and management. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10:728–739.
Materiały dla pacjentów po angielsku