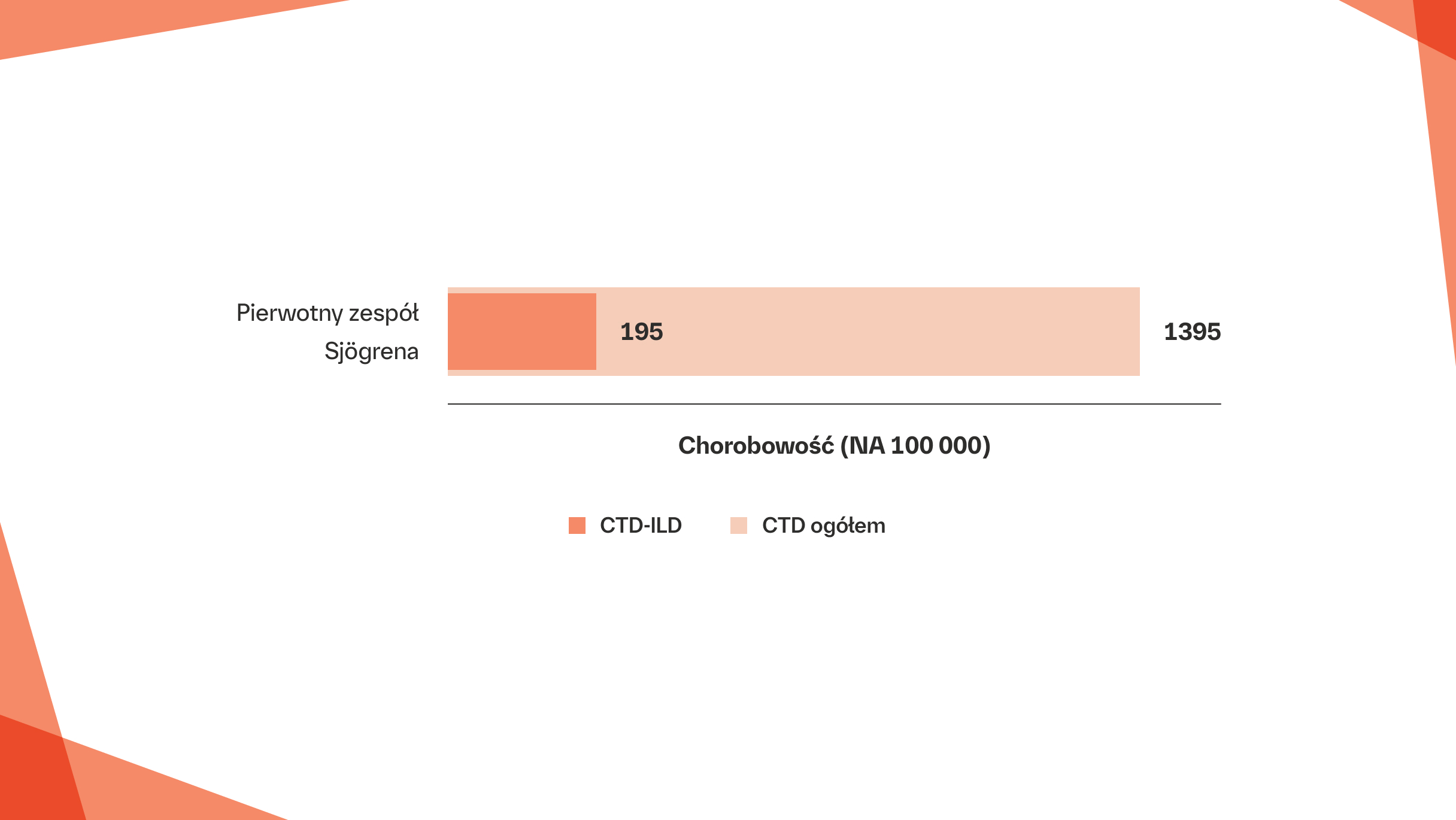
Rozpowszechnienie pSS‑ILD
Śródmiąższowa choroba płuc (ILD) rozwija się nawet u 20% pacjentów z pierwotnym zespołem Sjögrena (pSS)1–4


Charakterystyka typowego pacjenta z pSS-ILD 3,8,11,12



Pacjenci z ILD w przebiegu pSS są na ogół płci żeńskiej i palą papierosy:3
Mimo, że u mężczyzn z pSS występuje stosunkowo większe ryzyko rozwoju ILD niż u kobiet, typowy pacjent z pSS-ILD to zazwyczaj kobieta, ponieważ pSS występuje 13 razy częściej u kobiet niż u mężczyzn3,8
pSS z ILD jest 8 razy bardziej prawdopodobna w przypadku palenia tytoniu i 3 razy bardziej prawdopodobna w przypadku dodatniego wyniku testu na obecność ANA3
Jaki wpływ może mieć ILD na pacjentów z RZS i jak można zidentyfikować to zagrożenie?
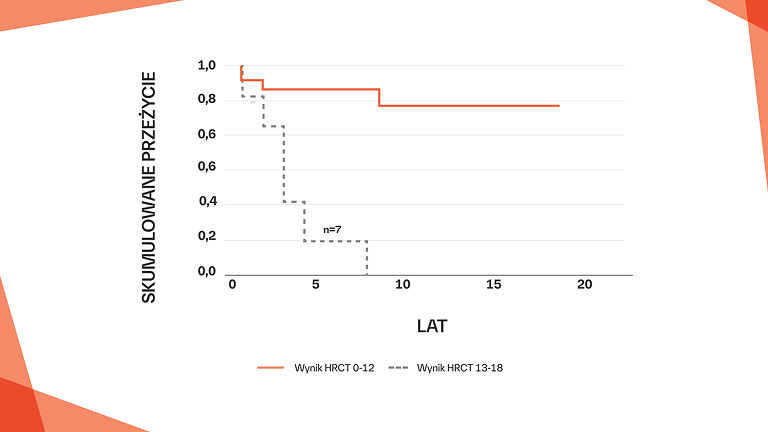
Skutki pSS‑ILD

Badania przesiewowe w kierunku ILD w pSS

Rozpoznanie pSS‑ILD
Przypisy
-
ANA: przeciwciała przeciwjądrowe; HRCT: tomografia komputerowa wysokiej rozdzielczości; ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc; OR: iloraz szans; pSS: pierwotny zespół Sjögrena; pSS-ILD: śródmiąższowa choroba płuc związana z pierwotnym zespołem Sjögrena.
-
Watanabe M, Naniwa T, Hara M, et al. Pulmonary manifestations in Sjögren’s syndrome: correlation analysis between chest computed tomographic findings and clinical subsets with poor prognosis in 80 patients. J Rheumatol. 2010;37(2):365–373.
-
Sambataro G, Ferro F, Orlandi M, et al. Clinical, morphological features and prognostic factors associated with interstitial lung disease in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A systematic review from the Italian Society of Rheumatology. Autoimmun Rev. 2020;19(2):102447.
-
Ramos-Casals M, Brito-Zerón P, Seror R, et al. Characterization of systemic disease in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: EULAR-SS Task Force recommendations for articular, cutaneous, pulmonary and renal involvements. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(12):2230–2238.
-
Roca F, Dominique S, Schmidt J, et al. Interstitial lung disease in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(1):48–54.
-
Guisado-Vasco P, Silva M, Duarte-Millán M A, et al. Quantitative assessment of interstitial lung disease in Sjögren’s syndrome. PLoS One. 2019;14(11):e0224772.
-
Alamanos Y, Tsifetaki N, Voulgari PV, Venetsanopoulou AI, Siozos C, Drosos AA. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in north-west Greece, 1982–2003. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006;45(2):187–191.
-
Patel R, Shahane A. The epidemiology of Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:247–255.
-
Wang Y, Hou Z, Qiu M, Ye Q. Risk factors for primary Sjögren syndrome-associated interstitial lung disease. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10(4):2108–2117.
-
Dong X, Zhou J, Guo X, et al. A retrospective analysis of distinguishing features of chest HRCT and clinical manifestation in primary Sjögren’s syndrome-related interstitial lung disease in a Chinese population. Clin Rheumatol. 2018;37(11):2981–2988.
-
Nannini C, Jebakumar AJ, Crowson CS, et al. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome 1976–2005 and associated interstitial lung disease: a population-based study of incidence and mortality. BMJ Open. 2013;3(11):e003569.
-
Zhang T, Yuan F, Xu L, Sun W, et al. Characteristics of patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome associated interstitial lung disease and relevant features of disease progression. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(5):1561–1568.
-
Sogkas G, Hirsch S, Olsson KM, et al. Lung involvement in primary Sjögren’s syndrome—an under-diagnosed entity. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:332.
-
Yazisiz V, Göçer M, Erbasan F, et al. Survival analysis of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome in Turkey: a tertiary hospital-based study. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39(1):233–241.
-
Lee AS, Scofield RH, Hammitt KM, et al. Consensus guidelines for evaluation and management of pulmonary disease in Sjögren’s. Chest. 2020 Oct 20. doi: 10.1016/j. chest.2020.10.011.
-
Li X, Xu B, Ma Y, et al. Clinical and laboratory profiles of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in a Chinese population: a retrospective analysis of 315 patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015;18(4):439–446.
Materiały dla pacjentów po angielsku