Wstępna ocena ILD
Możliwie jak najwcześniejsza identyfikacja włóknienia płuc u pacjentów może pomóc w zmniejszeniu ich obciążenia chorobą, spowolnić pogarszanie się codziennego funkcjonowania i jakości życia oraz zmniejszyć ryzyko przedwczesnego zgonu1–4

U pacjentów z grupy ryzyka należy wykonać badanie HRCT przy pierwszym podejrzeniu ILD, jeśli to właściwe, przy wyjściowym rozpoznaniu w przypadku podstawowej choroby tkanki łącznej (CTD), a następnie badanie to należy powtórzyć po stwierdzeniu pogorszenia się wyników PFT lub nasilenia się objawów oddechowych.5–9
OBJAWY PRZEDMIOTOWE I PODMIOTOWE SKŁANIAJĄCE DO PODEJRZENIA IPF
Chorobę należy podejrzewać u pacjenta zwykle w wieku ponad 60 lat, z dusznością wysiłkową, nieproduktywnym kaszlem, palcami pałeczkowatymi, a także z najbardziej charakterystycznym objawem – trzeszczeniami typu „taśmy rzepowej” w badaniu osłuchowym.10–12




OBJAWY PRZEDMIOTOWE I PODMIOTOWE ILD TYPU INNEGO NIŻ IPF
OBRAZ KLINICZNY ZAPALENIA PŁUC WYNIKAJĄCEGO Z NADWRAŻLIWOŚCI (HP)
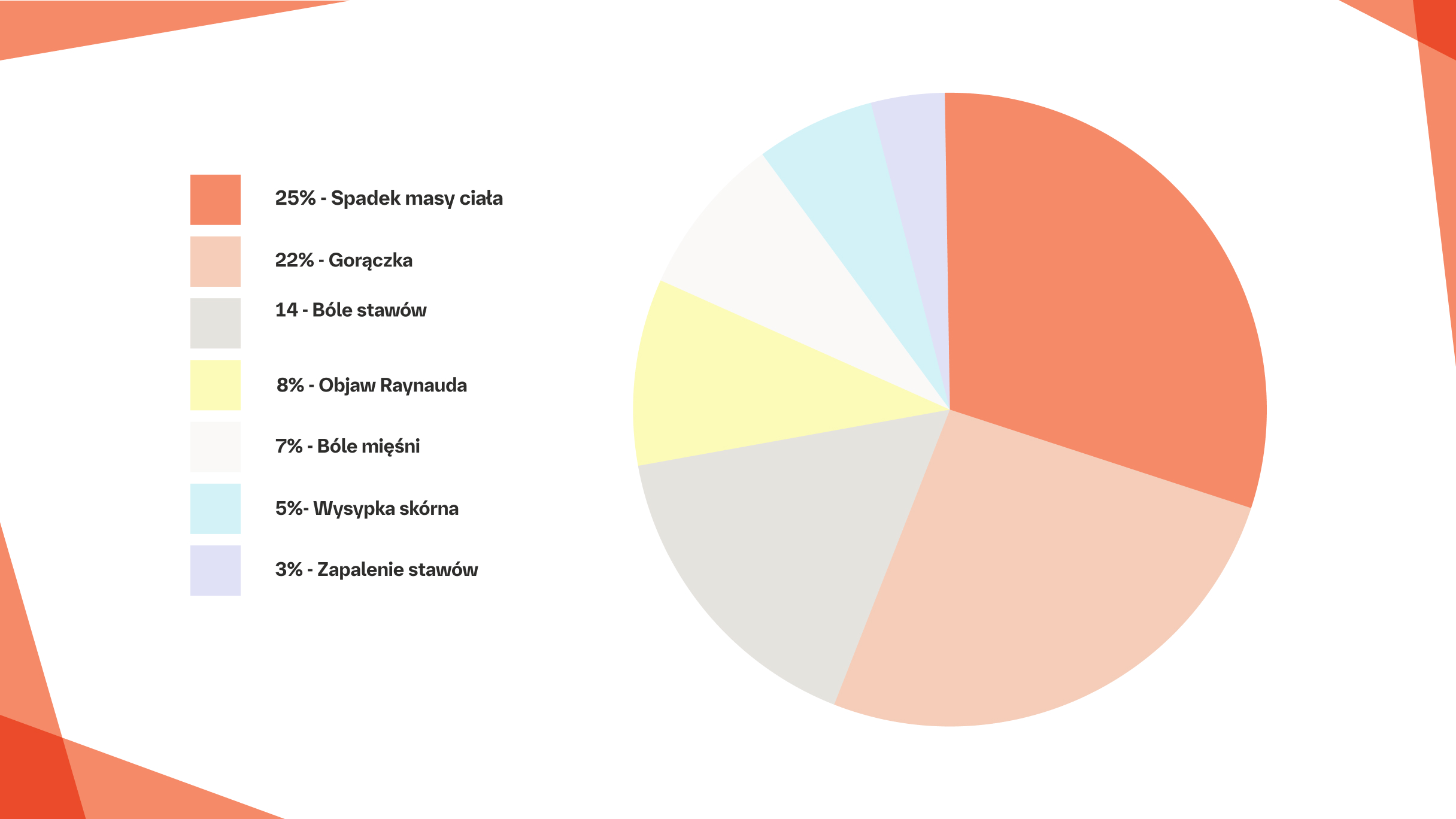
Podostre HP może przebiegać z gorączką, a podostre HP lub cHP może przebiegać z dusznością wysiłkową, kaszlem, zmęczeniem, złym samopoczuciem, jadłowstrętem i/lub utratą masy ciała.15
Badanie przedmiotowe zazwyczaj ujawnia przyspieszony oddech oraz trzeszczenia wdechowe u podstawy płuc.15 U niektórych pacjentów mogą występować świsty oddechowe.


POSTAĆ KLINICZNA ŚRÓDMIĄŻSZOWEJ CHOROBY PŁUC ZWIĄZANEJ Z SARKOIDOZĄ
Choroba śródmiąższowa płuc związana z sarkoidozą może objawiać się dusznością, kaszlem, bólem w klatce piersiowej i trzeszczeniami w płucach. Chorobę płuc można zwykle stwierdzić na podstawie nieprawidłowości w badaniu rentgenowskim klatki piersiowej:16
BADANIE PRZESIEWOWE POD KĄTEM ŚRÓDMIĄŻSZOWEJ CHOROBY PŁUC W PRZEBIEGU TWARDZINY UKŁADOWEJ (SSc‑ILD)
Zaleca się, aby u wszystkich pacjentów wykonywać badania przesiewowe w kierunku ILD w chwili rozpoznania SSc.7–9 Badania przesiewowe w kierunku ILD u pacjentów z SSc powinny obejmować dokładną ocenę kliniczną, w tym badanie obrazowe klatki piersiowej metodą HRCT, PFT, DLco i badanie osłuchowe.3,8,19,20
Więcej informacji na temat badań przesiewowych w kierunku ILD u pacjentów z SSc
BADANIE PRZESIEWOWE POD KĄTEM ŚRÓDMIĄŻSZOWEJ CHOROBY PŁUC W PRZEBIEGU REUMATOIDALNEGO ZAPALENIA STAWÓW (RZS‑ILD)
Zaleca się, aby u pacjentów z czynnikami ryzyka ILD lub objawami płucnymi wykonywać ocenę z badaniami PFT i HRCT w chwili rozpoznania RZS.21–24
W jaki sposób można wykonywać badanie przesiewowe w kierunku ILD u pacjentów z RZS?
Jak można potwierdzić rozpoznanie ILD u pacjentów po ocenie przesiewowej?
Rozpoznanie ILD

Zespoły wielodyscyplinarne
-
Chaudhuri N, Spencer L, Greaves M i wsp. A Review of the Multidisciplinary Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases: A Retrospective Analysis in a Single UK Specialist Centre. J Clin Med. 2016;5(66):1–9.
-
Cottin V, Hirani N, Hotchkin D i wsp. Presentation, diagnosis and clinical course of the spectrum of progressive-fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir Rev. 2018;27(150):180076.
-
Cottin V, Brown KK. Interstitial lung disease associated with systemic sclerosis (SSc‑ILD). Respir Res. 2019a;20(1):13.
-
Wong AW, Ryerson C, Guler S. Progression of fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir Res. 2020:29;21(1):32.
-
Flaherty KR, Brown KK, Wells AU i wsp. Design of the PF-ILD trial: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial of nintedanib in patients with progressive fibrosing interstitial lung disease. BMJ Open Resp Res. 2017;4(1):e000212.
-
Theodore AC, Tseng C-H, Li N, Elashoff RM, Tashkin DP. Correlation of cough with disease activity and treatment with cyclophosphamide in scleroderma interstitial lung disease: findings from the Scleroderma Lung Study. Chest. 2012;142(3):614–621.
-
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Fretheim H, Halse AK i wsp. Tracking impact of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis in a complete nationwide cohort. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019;200:1258–1266.
-
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Maher TM, Philpot EE i wsp. The identification and management of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: evidence-based European consensus statements. The Lancet Rheumatology. 2020b;2:e71–e83.
-
Asano Y, Jinnin M, Kawaguchi Y i wsp. Diagnostic criteria, severity classification and guidelines of systemic sclerosis: Guideline of SSc. J Dermatol. 2018;45, 633–691.
-
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ i wsp.; w imieniu Komitetu ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT ds. Idiopatycznego Włóknienia Płuc. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183(6):788–824.
-
Molina-Molina M, Aburto M, Acosta O i wsp. Importance of early diagnosis and treatment in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Exp Rev Resp Med. 2018;12(7):537–539.
-
Oldham JM, Noth I. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: early detection and referral. Respir Med. 2014;108(6):819–829.
-
Travis WD, Hunninghake G, King Jr TE i wsp. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: report of an American Thoracic Society project. Am J Respir Care Med. 2008;177:1338–1347.
-
Tomassetti S, Ryu JH, Piciucchi i wsp. Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: What Is the Optimal Approach to Management? Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;37:378–394.
-
Selman M, Buendia-Roldan I. Immunopathology, diagnosis, and management of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33:543–554.
-
American Thoracic Society. Statement on sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, luty 1999. Am J Respir Med. 1999;160:736–755.
-
Ianuzzi MC, Sah BP. Sarcoidosis. Merck Manual Professional Version website. Informacje dostępne pod adresem: https://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/pulmonary-disorders/sarcoidosis/sarcoidosis. Sierpień 2017. Dostęp: Listopad 2020.
-
Patterson KC, Strek ME. Pulmonary fibrosis in sarcoidosis. Clinical features and outcomes. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2013;10:362–370.
-
Roofeh D, Jaafar S, Vummidi D, Khanna D. Management of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2019;31(3):241–249.
-
Hoffmann-Vold A, Aalokken TM, Lund MB i wsp. Predictive Value of Serial High-Resolution Computed Tomography Analyses and Concurrent Lung Function Tests in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015;67:2205–2212.
-
Esposito AJ, Chu SG, Madan R i wsp. Thoracic manifestations of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chest Med. 2019;40(3):545–560.
-
Wallace B, Vummidi D, Khanna D. Management of connective tissue diseases associated interstitial lung disease: a review of the published literature. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2016;28(3):236–245.
-
Cottin V and Cordier JF. Subclinical interstitial lung disease: no place for crackles? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;186(3):289–290.
-
Lake F and Proudman S. Rheumatoid arthritis and lung disease: from mechanisms to a practical approach. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;35(2):222–238.
-
Wijsenbeek M, Cottin V. Spectrum of Fibrotic Lung Diseases. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:958–968.
Materiały dla pacjentów po angielsku